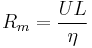Magnetic Reynolds number
The Magnetic Reynolds number is a dimensionless group that occurs in magnetohydrodynamics. It gives an estimate of the effects of magnetic advection to magnetic diffusion, and is typically defined by:
where
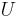 is a typical velocity scale of the flow
is a typical velocity scale of the flow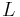 is a typical length scale of the flow
is a typical length scale of the flow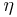 is the magnetic diffusivity
is the magnetic diffusivity
Contents |
General Characteristics for Large and Small 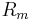
For 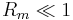 , advection is relatively unimportant, and so the magnetic field will tend to relax towards a purely diffusive state, determined by the boundary conditions rather than the flow.
, advection is relatively unimportant, and so the magnetic field will tend to relax towards a purely diffusive state, determined by the boundary conditions rather than the flow.
For 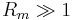 , diffusion is relatively unimportant on the length scale
, diffusion is relatively unimportant on the length scale 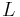 . Flux lines of the magnetic field are then advected with the fluid flow, until such time as gradients are concentrated into regions of short enough length scale that diffusion can balance advection.
. Flux lines of the magnetic field are then advected with the fluid flow, until such time as gradients are concentrated into regions of short enough length scale that diffusion can balance advection.
Relationship to the Reynolds Number and Péclet Number
The Magnetic Reynolds number has a similar form to both the Péclet number and the Reynolds number. All three can be regarded as giving the ratio of advective to diffusive effects for a particular physical field, and have a similar form of a velocity times a length divided by a diffusivity. The magnetic Reynolds number is related to the magnetic field in an MHD flow, while the Reynolds number is related to the fluid velocity itself, and the Péclet number a related to heat. The dimensionless groups arise in the non-dimensionalization of the respective governing equations, the induction equation, the momentum equation, and the heat equation.
See also
|
|||||
References
- Weisstein, Eric W., Magnetic Reynolds Number from ScienceWorld.
- Moffatt, H. Keith, 2000, Reflections on Magnetohydrodynamics. In: Perspectives in Fluid Dynamics (ISBN 0-521-53169-1) (Ed. G.K. Batchelor, H.K. Moffatt & M.G. Worster) Cambridge University Press, p347-391.
- P. A. Davidson, 2001, "An Introduction to Magnetohydrodynamics" (ISBN 0-521-79487-0), Cambridge University Press.